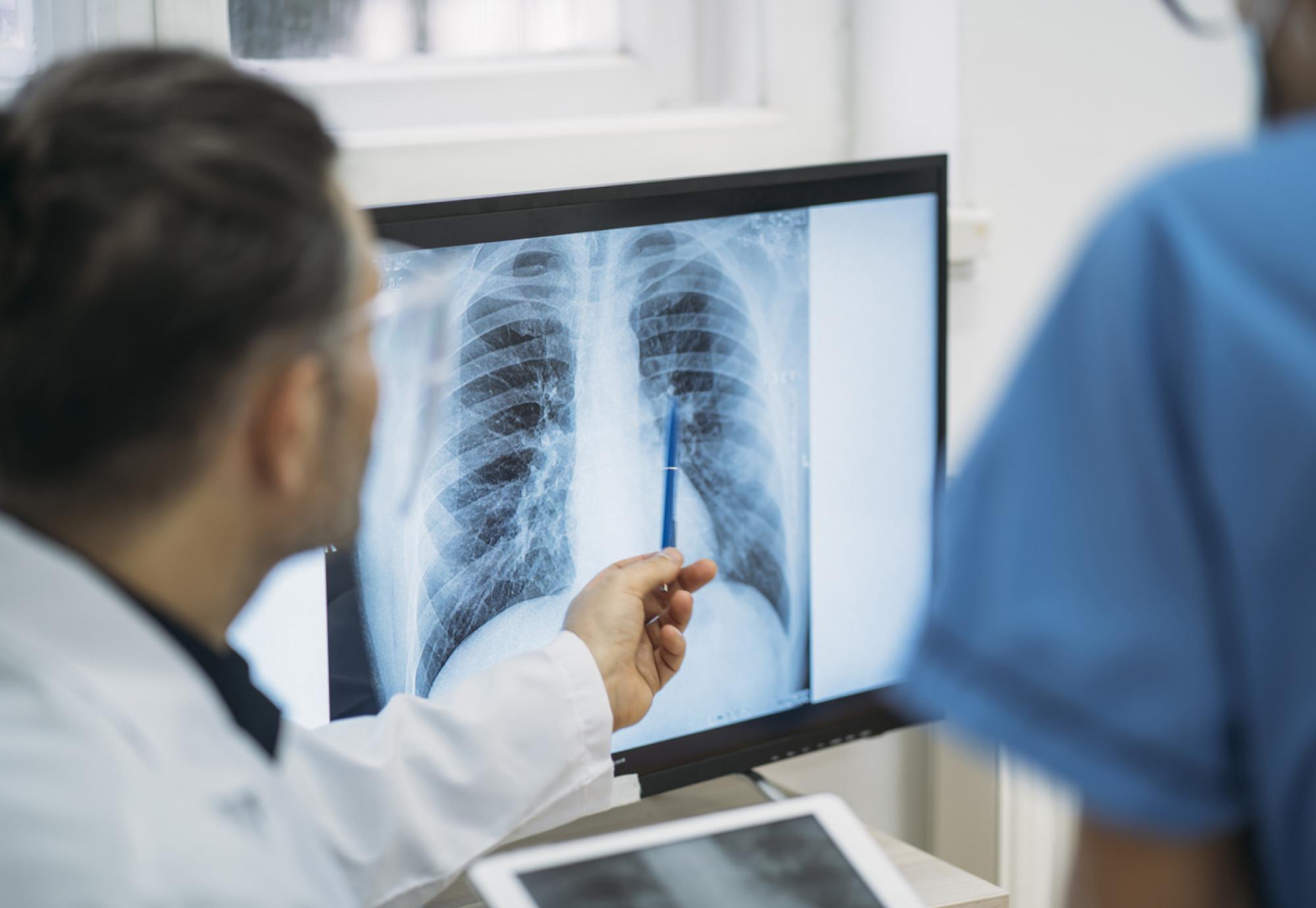
A new AI software is as effective as doctors are for analysing x-rays and diagnosing medical issues, a new study led by the University of Warwick and King’s College London has shown.
The AI, known as X-Raydar, was trained on 2.8 million historic chest x-rays from more than 1.5 million patients.
X-Raydar demonstrated comparable – if not better – results when put against the analysis of doctors at the time of the original x-ray for 35 out of 37 (94%) conditions.
To verify their findings, the research team took a sample of around 1,400 of the x-rays analysed by the AI and tasked a group of senior radiologists to cross-examine them.
The software scans x-rays as soon as they are taken and flags any abnormalities with an associated percentage. It can also understand the seriousness of different conditions, alerting doctors as necessary.
Dr Giovanni Montana, a data science professor at Warwick University, explained how this can help eliminate elements of human error.
He said: “If a patient is referred for an X-ray with a heart problem, doctors will inevitably focus on the heart over the lungs. This is totally understandable but runs the risk of undetected problems in other areas.
“This AI eliminates that human bias – it’s the ultimate second opinion.”
The researchers open sourced the entire AI software for non-commercial uses to accelerate research in this subject area.
The study’s co-author, Professor Vicky Goh, is the immediate past chair of the Academic Committee at the Royal College of Radiologists.
She said: “Current AI programmes available to us in the NHS only have a limited scope. Comprehensive AI programmes like this will be the future of medicine, with AI acting as a co-pilot for busy doctors.
“With the acute shortage of radiologists in the UK, programmes like this will facilitate interpretation and reduce delays for diagnosis and treatment.”
A recent Royal College of Radiologists report found that shortages in the sector were causing longer waiting times and thus delays in treatment at 97% of the UK’s cancer treatment centres.
The researchers also highlighted how the AI could improve efficiency for radiologists by identifying the x-rays which showed no abnormalities, ultimately allowing staff to focus on more critical demands.
The project was funded by a Wellcome Trust Innovator Award.
Image credit: iStock